-
#21. Improvise a Jazz Solo with an LSTM Network연구실 2019. 10. 24. 21:29
* Problem statement
(1) Dataset
- X: (m, Tx, 78), m개의 training example은 Tx = 30의 musical 값으로 이루어져 있으며, 각 time step에서 input은 78개의 one-hot vector로 이루어진 값이다. 따라서 x[i, t, :]는 i번째 예시에서 t 시간일 때 one-hot vector이다.
- Y: X와 거의 같지만 X보다 이전 단계를 나타낸다.
- n_values: 데이터셋에서 unique한 값, 여기선 78.
- indices_values: 0-77까지의 musical value들을 파이썬 딕셔너리로 매핑한 값.
(2) Overview of our model
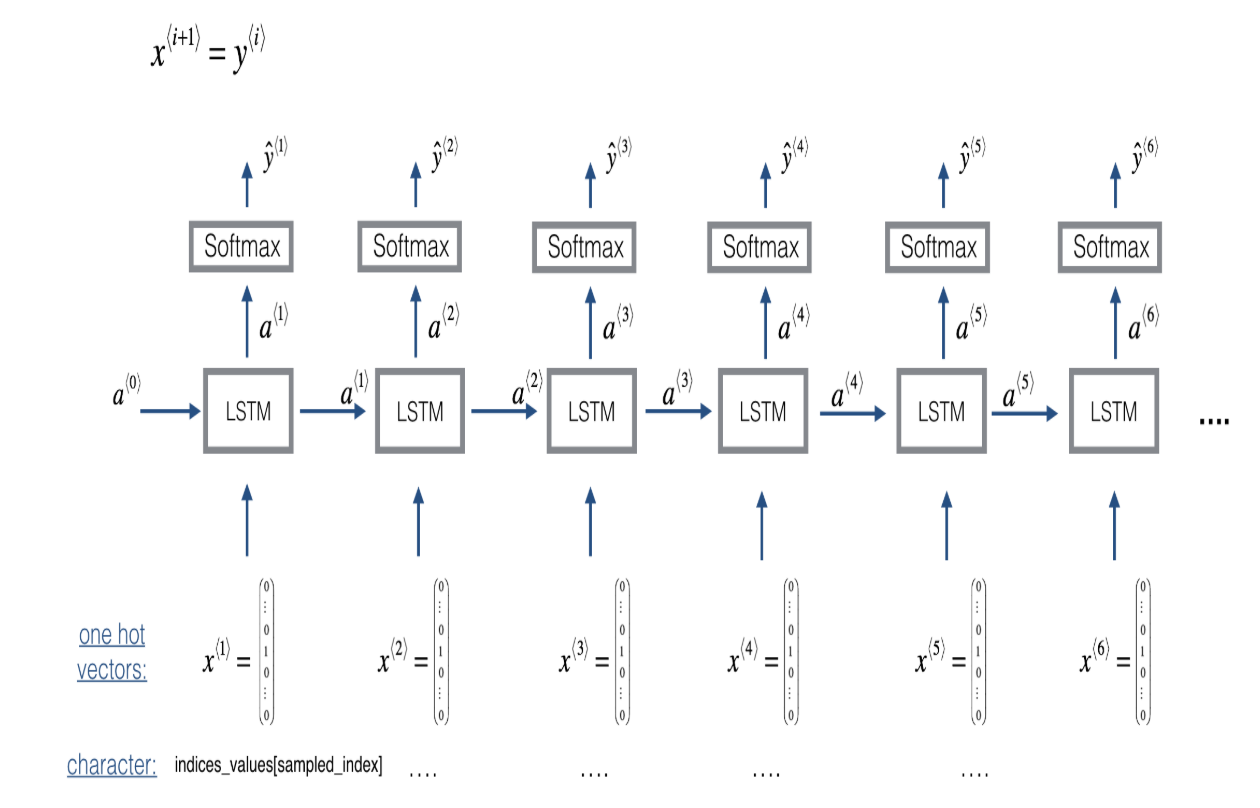
* Building the model
- X는 (m, Tx, 78), Y는 (Ty, m, 78), LSTM의 hidden state는 64차원을 사용할 것이므로 n_a = 64
- Keras에서 sequence가 input으로 들어왔을 때 output으로 label이 주어지는 built-in 함수는 존재하나, sequence generation에 대해서는 test time에 모든 x<t> 값을 미리 알 수 없다. x<t> = y<t-1>을 이용해 만들어주어야 하기 때문에 조금 더 복잡하다.
- global variable로 사용할 layers object를 정의해야 한다.
reshapor = Reshape((1, 78)) # Used in Step 2.B of djmodel(), below LSTM_cell = LSTM(n_a, return_state = True) # Used in Step 2.C densor = Dense(n_values, activation='softmax') # Used in Step 2.D# GRADED FUNCTION: djmodel def djmodel(Tx, n_a, n_values): """ Implement the model Arguments: Tx -- length of the sequence in a corpus n_a -- the number of activations used in our model n_values -- number of unique values in the music data Returns: model -- a keras model with the """ # Define the input of your model with a shape X = Input(shape=(Tx, n_values)) # Define s0, initial hidden state for the decoder LSTM a0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='a0') c0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='c0') a = a0 c = c0 ### START CODE HERE ### # Step 1: Create empty list to append the outputs while you iterate (≈1 line) outputs = [] # Step 2: Loop for t in range(Tx): # Step 2.A: select the "t"th time step vector from X. x = Lambda(lambda x: X[:,t,:])(X) # Step 2.B: Use reshapor to reshape x to be (1, n_values) (≈1 line) x = reshapor(x) # Step 2.C: Perform one step of the LSTM_cell a, _, c = LSTM_cell(x, initial_state=[a0, c0]) # Step 2.D: Apply densor to the hidden state output of LSTM_Cell out = densor(a) # Step 2.E: add the output to "outputs" outputs.append(out) # Step 3: Create model instance model = Model(inputs=[X, a0, c0], outputs=outputs) ### END CODE HERE ### return model- 모델 정의
model = djmodel(Tx = 30 , n_a = 64, n_values = 78)- 모델 컴파일
opt = Adam(lr=0.01, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.999, decay=0.01) model.compile(optimizer=opt, loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])- a0, c0 초기화
m = 60 a0 = np.zeros((m, n_a)) c0 = np.zeros((m, n_a))- 모델 피팅
m = 60 a0 = np.zeros((m, n_a)) c0 = np.zeros((m, n_a))* Generating music
(1) Predicting & Sampling
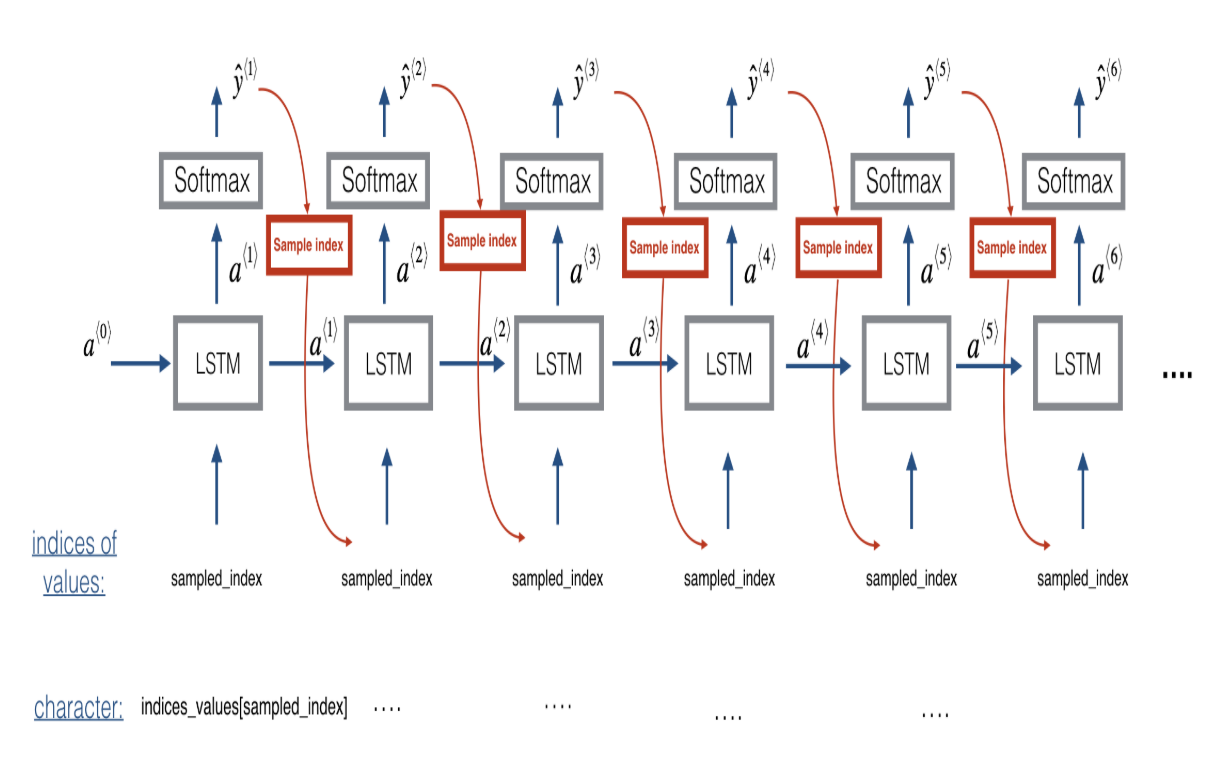
- 각 sampling 단계에 input은 activation a와 previous state에서 나온 cell state c이다. output 또한 activation과 cell state이다.
# GRADED FUNCTION: music_inference_model def music_inference_model(LSTM_cell, densor, n_values = 78, n_a = 64, Ty = 100): """ Uses the trained "LSTM_cell" and "densor" from model() to generate a sequence of values. Arguments: LSTM_cell -- the trained "LSTM_cell" from model(), Keras layer object densor -- the trained "densor" from model(), Keras layer object n_values -- integer, umber of unique values n_a -- number of units in the LSTM_cell Ty -- integer, number of time steps to generate Returns: inference_model -- Keras model instance """ # Define the input of your model with a shape x0 = Input(shape=(1, n_values)) # Define s0, initial hidden state for the decoder LSTM a0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='a0') c0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='c0') a = a0 c = c0 x = x0 ### START CODE HERE ### # Step 1: Create an empty list of "outputs" to later store your predicted values (≈1 line) outputs = [] # Step 2: Loop over Ty and generate a value at every time step for t in range(Ty): # Step 2.A: Perform one step of LSTM_cell (≈1 line) a, _, c = LSTM_cell(x, initial_state=[a0, c0]) # Step 2.B: Apply Dense layer to the hidden state output of the LSTM_cell (≈1 line) out = densor(a) # Step 2.C: Append the prediction "out" to "outputs". out.shape = (None, 78) (≈1 line) outputs.append(out) # Step 2.D: Select the next value according to "out", and set "x" to be the one-hot representation of the # selected value, which will be passed as the input to LSTM_cell on the next step. We have provided # the line of code you need to do this. x = Lambda(one_hot)(out) # Step 3: Create model instance with the correct "inputs" and "outputs" (≈1 line) inference_model = Model(inputs = [x0, a0, c0], outputs = outputs) ### END CODE HERE ### return inference_model# GRADED FUNCTION: predict_and_sample def predict_and_sample(inference_model, x_initializer = x_initializer, a_initializer = a_initializer, c_initializer = c_initializer): """ Predicts the next value of values using the inference model. Arguments: inference_model -- Keras model instance for inference time x_initializer -- numpy array of shape (1, 1, 78), one-hot vector initializing the values generation a_initializer -- numpy array of shape (1, n_a), initializing the hidden state of the LSTM_cell c_initializer -- numpy array of shape (1, n_a), initializing the cell state of the LSTM_cel Returns: results -- numpy-array of shape (Ty, 78), matrix of one-hot vectors representing the values generated indices -- numpy-array of shape (Ty, 1), matrix of indices representing the values generated """ ### START CODE HERE ### # Step 1: Use your inference model to predict an output sequence given x_initializer, a_initializer and c_initializer. pred = inference_model.predict([x_initializer, a_initializer, c_initializer]) # Step 2: Convert "pred" into an np.array() of indices with the maximum probabilities indices = np.argmax(pred, axis = -1) # Step 3: Convert indices to one-hot vectors, the shape of the results should be (Ty, n_values) results = to_categorical(indices, num_classes=n_values) ### END CODE HERE ### return results, indices'연구실' 카테고리의 다른 글
#23. Emojify (0) 2019.10.28 #22. Operations on word vectors (0) 2019.10.26 #20. Dinosaur Island - Character-Level Language Modeling (0) 2019.10.24 #19. Building your Recurrent Neural Network - Step by Step (0) 2019.10.23 #18. Face Recognition for the Happy House (0) 2019.10.18